A New Paradigm, Beyond the Limits of Cloud
- The Beginning and Future of Sky Computing

Sky Computing represents a new paradigm that seamlessly integrates complex cloud environments, enabling efficient utilization of resources as if they were a single platform. SkyPilot, the implementation of this concept, optimizes the execution of diverse workloads - ranging from AI and LLMs to other applications - across multi-cloud environments at the most cost-effective rates. By enabling SkyPilot to support SCP, Samsung SDS delivers enhanced cloud usability and cost optimization. Furthermore, Samsung SDS introduces SkyPlane for large-scale data transfer and SkyAirflow for multi-cloud workflow execution.
What Are the Key Technologies Required for Complex Cloud Environments?
Today’s cloud infrastructure has grown increasingly complex, far beyond what we could have imagined. Major cloud providers like AWS, GCP, and Azure operate across dozens of regions, hundreds of availability zones, and offer over 500 instance types, along with a variety of pricing models such as On-demand, Reserved, and Spot. For workloads* that require massive computational resources, such as AI, it is essential to leverage multiple clouds, diverse hardware, and sophisticated pricing models simultaneously. Even seemingly straightforward requirements, such as “executing tasks in the cheapest region**” can result unnecessary engineering resource expenditure and increased costs.
*Workload: Refers to all tasks that consume compute, storage, memory, or network resources, including applications, services, functions, or processes.
**Region: An independent infrastructure area where a cloud service provider groups multiple data centers (or availability zones) within the same geographic region.
To address this complexity, the Sky Computing Lab at UC Berkeley proposed Sky Computing. Sky Computing is a new paradigm that integrates multiple cloud infrastructures into a single unified pool, enabling users to utilize various cloud resources as if they were on a single platform. Its core principles are twofold: First, through a unified interface, users can define tasks once and execute them consistently across multiple clouds. Second, an embedded optimization engine analyzes pricing and availability in real time to automatically select the optimal infrastructure for each workload. This simplifies cloud usage, reduces costs, and allows access to a broader resource pool.
The Beginning of Sky Computing: Revolutionizing Multi-Cloud with SkyPilot
SkyPilot is the first open-source framework implemented by the Sky Computing Lab to realize the concept of Sky Computing. It enables the seamless execution of various workloads, including LLMs, AI, data science, and batch jobs, on any cloud platform. Additionally, it optimizes costs by identifying and utilizing the most cost-effective cloud for each task.
The initial release, version v0.1.1, was launched in the latter half of 2022, and over two and a half years have since passed. In the first half of 2023, the Cloud Research Team at Samsung SDS Research developed a feature for SkyPilot to support SCP (Samsung Cloud Platform, Samsung SDS’s enterprise cloud). By the second half of 2023, SCP was added as a newly supported cloud in version v0.4.0. SCP became the sixth cloud platform to be added after AWS, GCP, Azure, IBM, and Lambda Cloud, bringing the total number of supported clouds to 15.
However, with the release of version v0.5.0 in the first half of 2024, SkyPilot’s new sub-project called SkyServe was introduced, leading to a complete overhaul of SkyPilot's architecture. The new version, referred to as SkyPilot v2 (The development project version v2, based on the release version, is designated as v2 starting from v0.5.0), was released. As a result, any new clouds added had to be developed in alignment with SkyPilot v2's architecture. Since SCP was introduced prior to the release of SkyPilot v2's architecture, it was developed and integrated based on the legacy architecture.
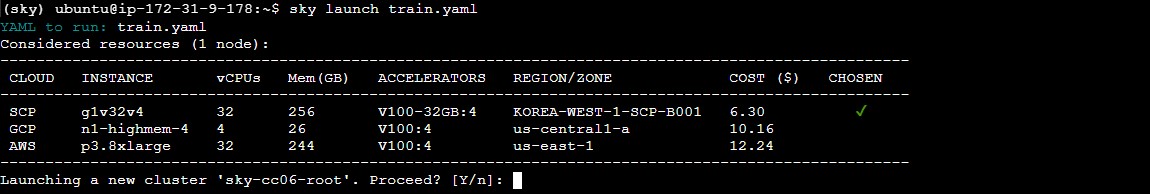 [Figure 1] Selecting the most cost-effective cloud among AWS, GCP, and SCP.
[Figure 1] Selecting the most cost-effective cloud among AWS, GCP, and SCP.
Since SCP was developed prior to the introduction of the SkyPilot v2 architecture, it initially lacked support for the SkyServe* feature. However, by the first half of 2025, the SCP support code was successfully developed for the SkyPilot v2 architecture and contributed to the official SkyPilot GitHub as an open-source project. This updated implementation, built on the SkyPilot v2 architecture, now enables the SkyServe feature, as depicted in Figure 2. *SkyServe: The model serving framework integrated into SkyPilot enables the deployment and operation of AI·LLM models simultaneously across multiple regions and clouds within a Sky Computing environment. By adding a serving layer to the "unified computing pool accessible anywhere," a core goal of Sky Computing, it enhances cost efficiency and availability.
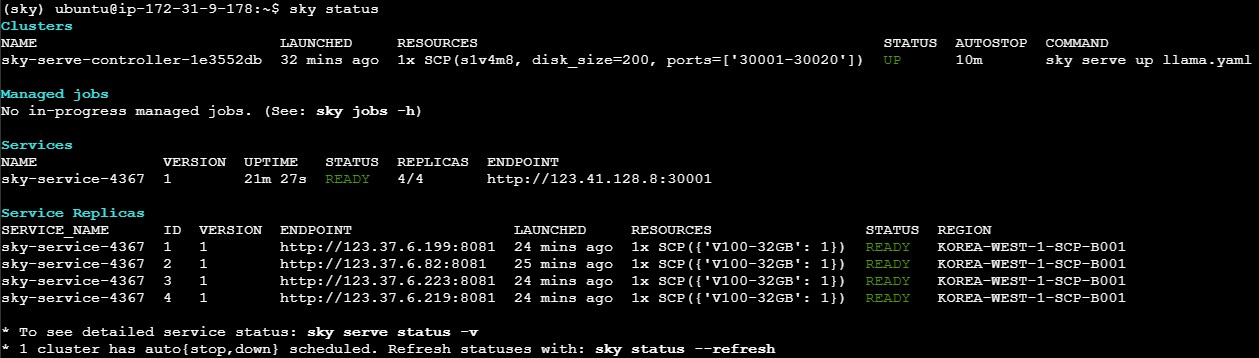 [Figure 2] Performing SkyServe in SCP
[Figure 2] Performing SkyServe in SCP
In the execution screen of Figure 2, it is observed that 1 Controller* and 4 Replicas* are all using SCP instances. The Controller receives the user's prompt, employs load balancing** to forward it to one of the four Replicas, and subsequently delivers the generated response back to the user. The Replica executes the LLM model to produce a response to the input prompt.
*Controller, Replica: The Controller receives user responses, creates Replicas to handle actual services, and dynamically adjusts the number of Replicas based on traffic volume through auto-scaling functionality. This ensures continuous service availability and performs load balancing across Replicas. Replicas are distributed across multiple regions and clouds, all under the control of the Controller.
**Load Balancing: A technology that evenly distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers (or computing resources) to prevent overloading of a single server and optimize application availability and responsiveness.
As a result, the SCP support feature developed under the SkyPilot v2 architecture has been confirmed to function correctly. Furthermore, starting from version v0.8.0, a feature was introduced to monitor batch jobs in real-time on a dashboard. In the dashboard depicted in Figure 3, you can observe the execution of tasks across AWS, GCP, and SCP.
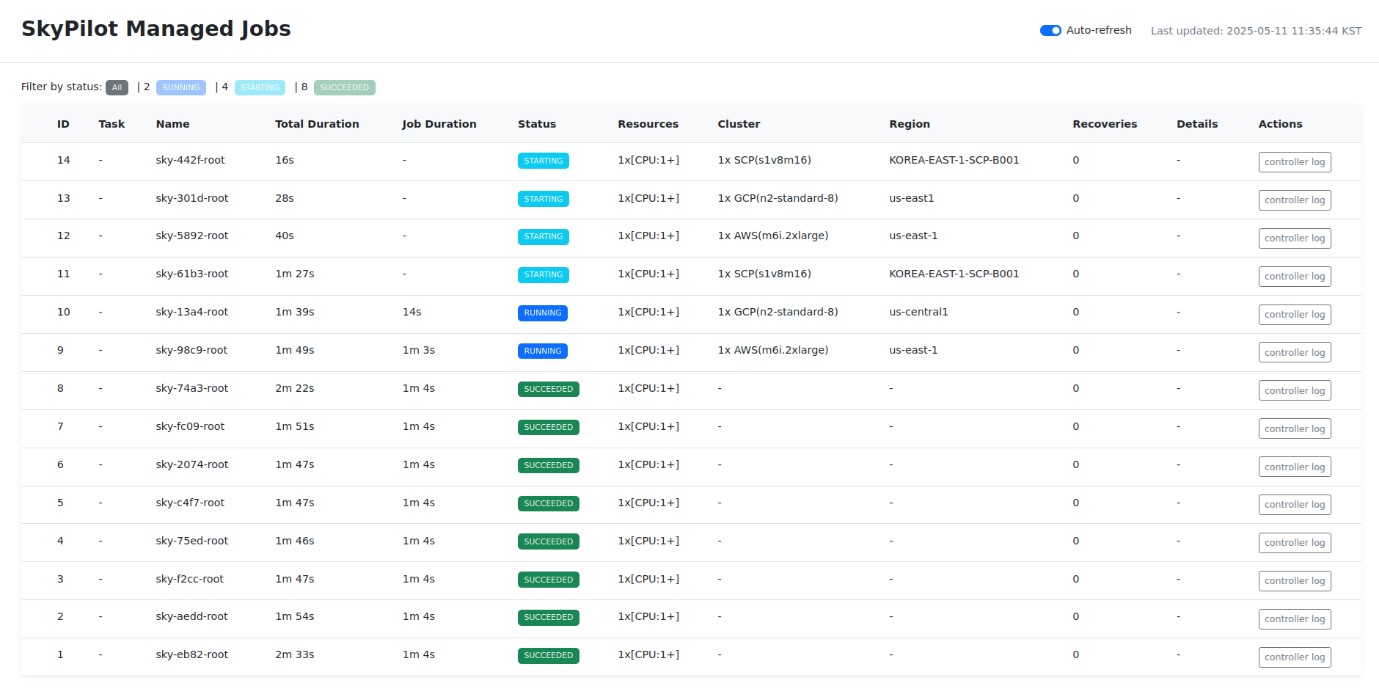 [Figure 3] Dashboard showing tasks executed on AWS, GCP, and SCP
[Figure 3] Dashboard showing tasks executed on AWS, GCP, and SCP
By offering a dashboard feature that conveniently visualizes both ongoing and completed tasks, managing and executing tasks across multiple clouds has become significantly more efficient.
Efficient and Seamless Large-Scale Data Transfer
Next, let's discuss SkyPlane. SkyPlane is an open-source project designed to transfer large volumes of data quickly and efficiently in cloud environments. The core objective of this project is to enable cost-effective movement of large-scale data between various cloud object storages, such as AWS, GCP, and Azure.
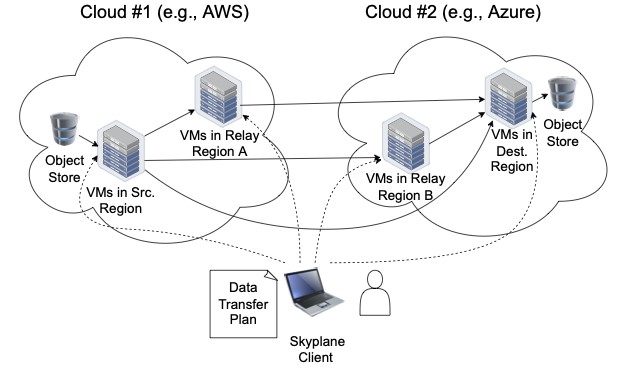 [Figure 4] VM provisioning and overlay network (출처: https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.07259)
[Figure 4] VM provisioning and overlay network (출처: https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.07259)
To maximize transfer speed, SkyPlane automatically provisions* multiple virtual machines in the cloud to compress and transmit data in parallel. During this process, it minimizes costs by leveraging bandwidth tiering and compression techniques. The Cloud Research Team at Samsung SDS Research developed the SCP support feature in the latter half of 2023." *Provisioning: The entire process of creating, allocating, and configuring IT resources such as servers, storage, networks, and software to make them immediately usable upon user request.
All-in-One Multi-Cloud Workflow
In the first half of 2024, the Cloud Research Team at Samsung SDS Research proposed the SkyAirflow project to the Sky Computing Lab. SkyAirflow is an official provider package that enables the execution of multi-cloud workflows by offering SkyPilot as a provider for Apache Airflow*. This integration allows users to seamlessly perform tasks across various cloud platforms, including AWS, GCP, and SCP, within Airflow workflows using SkyPilot. * Apache Airflow: An open-source platform that enables the definition, scheduling, and monitoring of workflows (such as data, ETL, and ML pipelines) in the form of a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG).
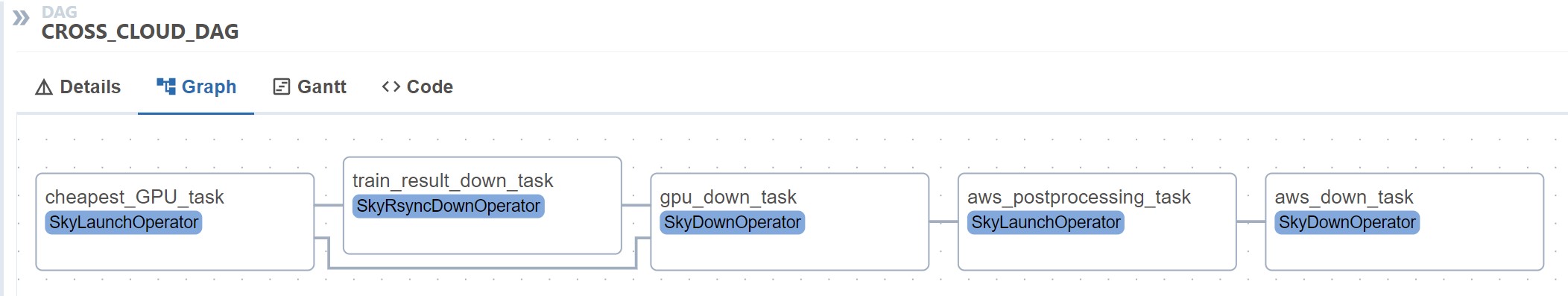 [Figure 5] Executing workflow using SkyAirflow
[Figure 5] Executing workflow using SkyAirflow
The Future Samsung SDS Research is Preparing for through Sky Computing
Users are always looking for ways to utilize cloud services more conveniently, cost-effectively, and with enhanced performance. In the future, it is anticipated that integration of multiple cloud services will become a standard practice. Samsung SDS Research's Sky Computing initiative embodies this vision, addressing user concerns and aligning with evolving expectations. Cloud services of the future will allow users to effortlessly request the desired service without needing to know the specific cloud platform or navigating complex processes. The service will be intelligently deployed and executed in the most optimal cloud environment, ensuring efficiency and performance. Of course, all information related to this process will be transparently shared with the user.
Open Sources
https://github.com/skypilot-org/skypilot
https://github.com/skyplane-project/skyplane
https://github.com/skypilot-sds/airflow-provider-skypilot