
Preface
Since the release of the World Wide Web in the early 1990s, the Internet has evolved rapidly and established itself as a communication network and communication medium that connects the world. In the meantime, we have gone through the times called Web 1.0 and Web 2.0, and now we are approaching the era of a new paradigm called Web 3.0. However, opinions on the concept and substance of Web 3.0 are still divided. Even though Elon Musk, the CEO of Tesla, criticized "Web 3.0 is an illusion without substance," the market's interest in Web 3.0 is growing day by day. What is Web 3.0 and how is it evolving?
The Background of the Emergence of Web 3.0
In today's digital society, data is the most valuable resource and asset. However, individuals are only data providers, and only a few companies monopolize and utilize data to generate revenue. Let's look at the reasons why a small number of companies can monopolize data in the current web ecosystem and the background of the emergence of an alternative called Web 3.0 through the development process of the web.
Web 1.0
In 1991, Tim Berners-Lee, a British computer scientist, unveiled the World Wide Web to the world, opening the Web 1.0 era that would last until 2004. Web 1.0 was static web pages that could only be “read” and involved no interactions other than clicking. In other words, the majority of users could only read the limited form of content provided by a minority.
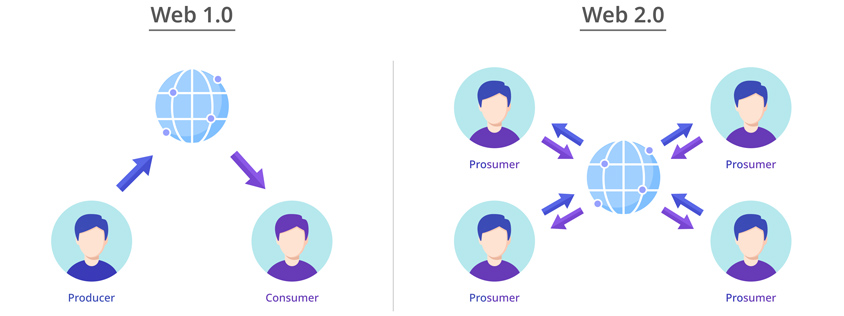
- producer -> web -> consumer
- multiple prosumers -> web -> multiple prosumers
Web 2.0
As we entered the 2000s, the web developed rapidly with the spread of the Internet and the diversification of devices. Users who were only able to “read” started to actively “participate” by “creating” and “sharing” content directly. Web 1.0 was a set of simple web pages that only allowed one-way communication, but Web 2.0, in which the web has evolved into platforms, enabled two-way communication.
With the spread of smartphones, Web 2.0 evolved once more. Users could always access the Internet and can freely share services between different devices or systems through platforms provided by companies. As a result, as the role of the platform grew, a small number of operators naturally led the web ecosystem. Platform operators, such as NAVER, Google, and Facebook provided various services for free with simple membership registration, and users began to actively utilize these services to communicate with each other and produce data.
Problems with Web 2.0
Web 2.0 platform operators took user data and the ownership in exchange for providing a varied, high-quality web environment. Companies that knew the value of data earlier grew by actively collecting data from service users and monopolizing most of the revenue generated from it. The data that keeps piling up has become a huge asset for companies, and as a result, the closed, centralized platform of Web 2.0 had unrestricted power to control users. In the meantime, Facebook's massive personal information leakage incidents have occurred, and social awareness of the value, importance, and security of personal information collected and managed by a small number of platforms has been strengthened.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0 begins with “Semantic Web,” a concept proposed by Tim Berners-Lee in 1998. Semantic Web refers to a web in which machines understand natural languages used by humans and provide personalized information that fit situations and context.
Web 3.0, which began to emerge with the problems with Web 2.0, includes “Semantic Web,” “Decentralized Web,” and a metaverse based on the protocol economy. Therefore, the current Web 3.0 refers to a new type of web ecosystem that uses semantic technology to provide personalized information and enables “personal data ownership” based on decentralization and data encryption through the blockchain system.
Semantic Web
While the keyword search feature of Web 2.0 required users to go through dozens of pages to find the information they wanted, the Semantic Web of Web 3.0 can remove unnecessary information and quickly derive personalized information based on the user's inclination and search purpose.
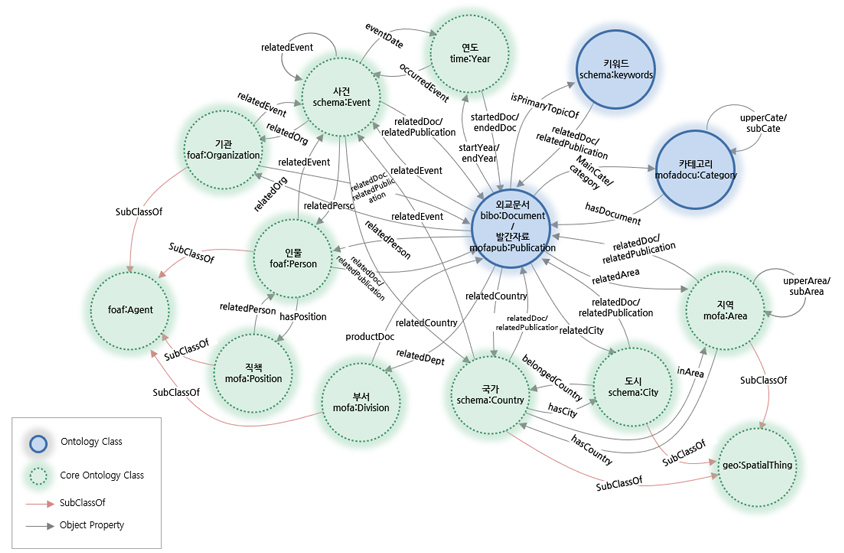
- ontology class: keyword(schem:keywords), category(mofadocu:category), diplomatic document(bibo:document)/publication(mofapub:publication)
- core ontology class: year (time:year), event (schema:event), organization (foaf:organization), person (foaf:person), foaf:agent, position (mofa:position), division (mofa: division), country (schema:country), city (schema:city), area (mafa:area), geo:spatialthing
- subclassof:foaf:agent <- organization (foaf:organization), person (foaf:person), position (mofa:position), division (mofa:division)
- object property: keywords (schem:keywords), category (mofadocu:category), year (time:year), event (schema:event), organization (foaf:organization), person (foaf:person), division (mofa:division), country (schema:country),city (schema:city), area (mafa:area) -> diplomatic document (bibo:document)/publication (mofapub:publication) <- keywords (schem:keywords), category (mofadocu:category), year (time:year), event (schema:event), organization (foaf:organization), person (foaf:person), division (mofa:division), country (schema:country),city (schema:city), area (mafa:area)
How can personalized information be provided? When we think of an apple, various related information, such as the color and type of apple, comes to mind. Such subsidiary information about the apple is called metadata. And the set of these metadata is the Ontology. Computers can think intelligently like humans through the process of conceptually connecting and analyzing data using ontology. Furthermore, they can provide personalized information by analyzing and learning users' search patterns.
Decentralization
In Web 2.0, the connection between users was possible only through a platform that acted as an intermediary, so the platform power naturally increased. The concept that emerged as resistance against this is the “decentralized web.” “Decentralization,” the most important keyword of Web 3.0, can be realized through a blockchain system.
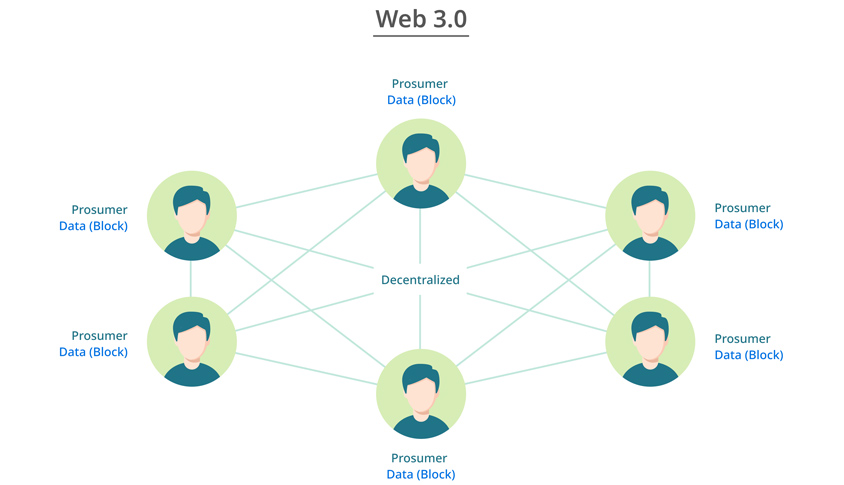
- multiple prosumers(data(block)) -> decentralized -> multiple prosumers(data(block))
- multiple prosumers(data(block)) -> multiple prosumers(data(block))
- prosumer(data(block)) -> prosumer(data(block))
Blockchain is a data distribution processing technology that distributes and stores data on each node based on the Peer-to-Peer (P2P) method, in which nodes are autonomously connected without a central server. Since data in the blockchain is managed by many unspecified nodes, there is no central administrator. Therefore, Web 3.0 can be freed from central control by encrypting data and allowing individuals to own it through an open, decentralized blockchain platform. Even now, decentralization is in progress in various ways, such as Decentralized Application (DApp), Decentralized Finance (Defi), and Decentralized Identity (DID).
Metaverse
In the past, the metaverse was simply a virtual space implemented in three dimensions, but with the addition of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) innovation, Web 3.0 evolved into a digital world where virtual reality and reality converge. The development of VR, AR, and MR technology is creating a new digital economy ecosystem, providing user experiences that blur the boundaries between reality and virtual reality and enabling proof of ownership of digital assets through NFTs. Metaverse is a space where economic and social activities are possible and a new life paradigm presented by Web 3.0, and commercialization attempts are being made in many fields. It would not be an exaggeration to say that there is a metaverse craze in almost every field, including the public sector and education, starting with the game and entertainment industries.
Web 3.0, is it the perfect future?
Web 3.0 presents an ideal utopian vision, but there are also some critical views. Is complete decentralization possible? Just as Facebook changed its name to “Meta” and jumped into the metaverse business, huge companies that used to lead Web 2.0 are now turning their eyes to Web 3.0. The development of blockchain technology that can be decentralized is also being led by huge companies. Because of this, some are concerned that Web 3.0 may become a new form of centralization rather than decentralization. In addition, there are numerous issues to consider, such as massive data processing technology and device advancement and distribution, management and utilization of personal information or data, and high barriers to entry for the general public without relevant knowledge. Steemit, a blockchain-based SNS that realized the tempting proposal of Web 3.0 to restore data sovereignty and return profits to users, became a space exclusively for profit and failed. There is a craze for metaverse and Play to Earn (P2E) , but this may not be too different from centralized Web 2.0 services. It is still necessary to spend a lot of time and money to realize the vision of Web 3.0, as well as in-depth social discussions.
Web 3.0, Lower the Barrier to Entry
Realizing Web 3.0 requires generic technologies, such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, AR/VR, distributed storage, and networks, but usability is important in successfully popularizing them. Sisun Lee, the co-founder of Ramper, a Web 3.0 infrastructure software developer, said, "If people who are new to blockchain wish to use the service and the first thing they have to do is “Connect Wallet,” it will be difficult to attract users, and it is difficult to popularize Web 3.0 with current user experience." In addition, Natalie Luu, who is responsible for the ecosystem development of Terra network, said, “Frictionless user experience is essential for the success of next-generation Web 3.0 services.” No matter how well-purposed a service is, if it is too user-driven or complicated, it will inevitably be shunned in the market. The concepts of Web 3.0, such as coin wallets, NFT creation and transactions, and the metaverse, are building high barriers to entry that requires users to learn at a certain level. For a complete transition to Web 3.0, it is also necessary to carefully consider ways to easily induce users accustomed to Web 2.0 to participate voluntarily.
Epilogue
As Tesla's Elon Musk and Twitter's Jack Dorsey have said, Web 3.0 may simply be a marketing term. However, it is clear that Web 3.0 is a reasonable alternative to solve the problems of centralized and monopolistic Web 2.0. The shift to Web 3.0 has already begun, with a series of active investments and technology developments from many companies. Change and development do not happen in an instant. Web 3.0 may become part of our lives through repeated failures and successes at some point, as Web 1.0 and 2.0.
Web 3.0 is a new paradigm that will bring changes throughout our lives and is a future that will definitely come.
References
[1] https://www.singlegrain.com/web3/web-3-0/
[2] https://www.etoday.co.kr/news/view/2105145
[3] https://it.donga.com/101672/
[4] https://magazine.hankyung.com/money/article/202202143142c
[5] https://www.blockchaintoday.co.kr/news/articleView.html?idxno=19706
[6] https://www.edaily.co.kr/news/read?newsId=02515766632263648&mediaCodeNo=257
▶ The content is protected by the copyright law and the copyright belongs to the author.
▶ The content is prohibited to copy or quote without the author's permission.

Software Business Division Development Platform Group of S-Core Co., Ltd.
He is in charge of UX/UI design at S-Core.
- Innovations in Contents Management to Keep Customers Stay Longer and Visit More Frequently
- Smart Office to Support Business Innovation
- Samsung SDS Earns Recognition as 2023 Asia-Pacific Climate Leaders
- The Chronicles of Cloud Computing
- Finding the Best Cloud Adoption Strategy
- Cloud-First Strategy to Accelerate Digital Transformation
