Digital transformation means business innovation based on digital technologies. AI has the biggest expected effect from among the technologies allowing business innovation. It is only difficult in the early stage when establishing the purpose, area, introduction method, and method to collect and use data. Once established, AI constantly evolves to provide better outcomes. In particular, RPA and AI agents applicable to general office work rather than AIs for grandiose production processes or manufacturing have greater expected effects, and as such, are easy to apply in a wider range of areas. The RPA and AI agents applicable to various office work leap to the next level of intelligent automation with cognitive automation.
Easier digital work through RPA
RPA means automation that uses software to perform tasks triggered by predefined sequences by the user. It is intelligent robot software, like the robots in a factory doing the work that's difficult for humans or facilitating the work process by assisting humans.
Of course, using RPA increases work efficiency and productivity. It helps finish work which used to take 3-4 hours in seconds, allowing humans to focus on creative and strategic high-value-added work. For example, RPA enables completing repetitious tasks that can take 10-20-minutes of work in 1 second, completing things like checking the data on ERP sales totals and sales volumes for each product for daily and weekly reports, entering figures in Excel files, and recording changes compared to the previous day and week.
Its greatest strength is that it reduces human errors to increase work accuracy. Especially for numbers, humans are not more accurate than a calculator. In calculation tasks, including for Excel files, if an individual enters the wrong number or symbol, it will be much more difficult to fix later on. Finding the wrongly entered figure or symbol is gruesome. Given that, the biggest expected effect of RPA is reducing mistakes and improving work accuracy to prevent accidents in advance. Companies can benefit from saving costs for repetitive, simple work by introducing RPA to focus on more productive tasks and increase the added-value.
 Samsung SDS Brity RPA
Samsung SDS Brity RPA
In fact, interest in RPA has already surged in all industries since 2017, and foreign companies have used RPA in various areas in general, including telecommunication companies and carriers, two years earlier than Korean companies. For example, Walmart uses 500 RPAs for tasks to respond to employees' questions and write documents, including searching and reviewing products and inventory checks. A Korean company, Coway, has applied RPA to over 40 tasks, including calculating sales performance, organizing overviews of rental assets, and reviewing billing, and has expanded its use after seeing a 50% increase in the overall process speed.
Major financial companies in Korea are also actively introducing RPAs. So they earned substantial results in work automation, including ID card verification of forgery upon customer registration, contactless bank account approval, and gathering the results of registered mail sent to customers. In manufacturing, RPA is actively introduced for processing client registration, data review for materials and production management, ERP registration, sales code-based data collection, corporate card history, travel expenses, and input tax invoices. In retail, the tool is used for handling inventory input, POS data input, and daily/monthly closing work.
Another well-known usage of RPA is chatbot services for customer service for online shopping malls, telecommunications companies, and financial companies. Advanced RPA, or artificial intelligence, also responds with the best possible answer to emails or texts from customers through chatbots by checking the manuals and customer information on behalf of customer service representatives. However, customers wouldn’t be satisfied if the robot service representatives delivered the best possible answer without reading their feelings and intentions. Therefore, RPA should assist humans rather than replace them to bring their best capabilities.
Like this, RPA is mainly used for calculations, including ERP and SCM, with enough performance to be applied throughout various tasks, including customer service. The success of RPA also led to a growth of RPA providers that offer such solutions. Well-known cases are Samsung SDS, UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism. The market is expected to grow with enterprise solution companies, such as IBM, Microsoft, and SAP, acquiring or signing partnership agreements with these RPA-dedicated companies.
Practical expected effects of RPA used in various areas
The financial industry has started introducing RPA and expanding its application from rule-based, repetitive simple work previously done manually. For example, they saw a decrease in inefficiencies for document review and loan evaluation in 2017 for loan work. RPA handles the work for humans and increases accuracy and saves time by reviewing documents, including copies of IDs, certificates of employment, and earned income withholding taxes, that are submitted by potential borrowers, and checking for any omitted documents. In particular, RPA can save overall time and provide faster loan services for customers with increased customer satisfaction when the number of loan applications suddenly spikes.
In fact, banks and card companies can see instant improvements in their work as the RPA handles so many processes, document and regulation reviews, and complex calculations. The lists of RPA solutions in the financial sector include automatic handling of loan documents issuance (proxy), utility bill cash disbursement, market price registration for calculating the maximum used car loan, documentation work for settlements of international transactions, and checking any regulation breach and sending emails and text messages. In some tasks, it can even handle all the work that used to be performed by humans. Sometimes, RPA alerts the customer of overspending by analyzing the balance and recommends good payment dates for credit cards or loans with the lowest interest rate without human intervention.
In the manufacturing industry, it emails people in charge when production or operation reaches the threshold while monitoring a factory or reviewing SBOM for managing materials and productions and entering the figures in ERP. For example, humans should check the products in multiple processes when delivering the products from factories to warehouses and then distribute them to available warehouses considering the weight and sizes of the products to be delivered. First, the factory employees should check the size, volume, and weight of the product in the factory. Then, they should look for the vehicle's capability, the driver information, the actual vehicle and driver, and the distance between the warehouse and the factory in the delivery system. They should also record the contact information of the driver. Finally, they should access the logistics system to learn about the current status of each warehouse to decide which warehouse would be the best choice considering the previously learned size and weight of the products. After that, they should inform the driver of the factory's location and the product's pickup point. After thousands of processes, checking, and rechecking, they should send a message to the driver. However, if RPA does this work for them, it will automatically look for the data recorded in each system and trigger a message to the driver.
The RPA involved in the hardware maintenance agreement slashes the time for manual, time-consuming tasks. For example, the sales department has to exchange materials with the agreement supporting department in multiple steps, checking and approving when signing an agreement. There are numerous steps: Once the materials are delivered from the Sales to General Affairs team, General Affairs reviews them according to the internal regulations. Then, General Affairs sends a draft to Sales, and Sales consults with the client about the draft and delivers it to General Affairs to get a final check. However, this complex process demanding multiple communications has introduced RPA to reduce intermediate processes. Once Sales sends materials to RPA, it automatically analyzes, evaluates, and approves the content and delivers them to General Affairs. The team just checks some complements, RPA takes over to deliver the draft to the client, and Sales receives the final version, and then RPA confirms whether to conclude the agreement or not and delivers the conclusion to General Affairs. While RPA handles simple repetitive tasks that used to be done manually, Sales and General Affairs can focus on more value-added work.
Marketing, too, uses RPA to greatly save time in writing monthly reports on product sales trends. When humans create a sales report, they need to log in to the ERP system and collect data through various processes to get the figures on the sales history for each product. The collected data should be input into the Excel file, and the figures should be organized so that it is easy to compare the data from the previous month and year. Then, marketers send messages to related persons, draw implications through meetings, and write and review reports. However, once RPA jumps into this progress, it collects related data and organizes graphs and basic analysis reports instead of the workers. Then, it triggers an email containing a report draft to related persons and holds a meeting. After that, the Marketing team takes over, reviews and organizes the reports during the meeting, and draws implications. In other words, RPA automatically processes the various tasks in earlier procedures, leaving marketers just checking the emails from RPA and attending the meetings to draw implications.
Evolving RPA to cognitive automation
At this point, looking at RPA in various applications, you may wonder what the differences are between RPA and AIs as well as RPA and macro programs. A macro program executes a series of pre-stored commands into a single routine. A slight difference from the pre-defined sequence prevents the macro from functioning well. That is, the macro does the work for repetitive typing tasks and clicks. On the other hand, RPA is an artificial intelligence-based technology that makes intelligent decisions in ever-changing situations and automates work where you need it. In summary, macro replaces the human tasks used in a structured order in sequence by computer, while RPA processes unstructured tasks through artificial intelligent in a smarter way.
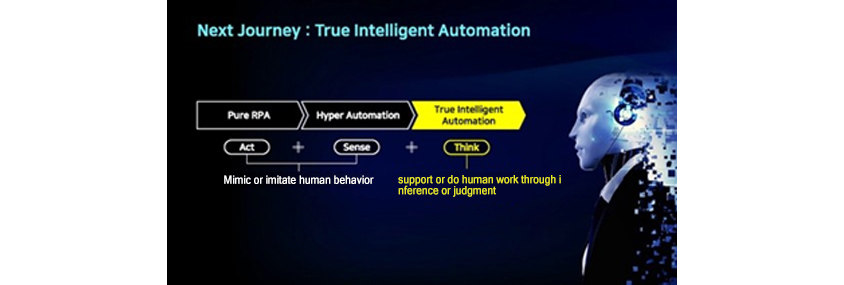
- pure RPA > hyper automation > true intelligent automation
- act + sense + think
- • Mimic or imitate human behavior, support or do human work through inference or judgment
In fact, AI is a more advanced form of universal, working RPA at the enterprise level. In other words, it can make RPA more intelligent and scale it up to a broader and long-term large-scale form to transform the processes and systems of a company. Therefore, AI requires a long-term and larger investment than RPA. In addition, AI is sometimes applied to RPA to enable working intelligently. This is called cognitive automation.
In fact, RPA is only one part of work process automation. In other words, RPA is the new version of innovation in enterprise informatization based on IT systems, following the path of ERP in the 1980s and PI, a process innovation, in the history of industrial development. That said, RPA is not in its final form. It will go further to go through yet another evolution. While PI seeks to achieve dramatic performance through innovation in the information system and work process based on ERP, RPA aims to maximize work efficiency and productivity by connecting existing IT systems with computers in individual workplaces.
In that sense, RPA will evolve into the complete form of AI in the future, and Cognitive Automation can play a practical role in the evolution of RPA in the process. In other words, the existing RPA does the automated tasks across multiple and complex systems based on predefined rules. However, RPA incorporated with Samsung SDS’ Cognitive Automation, will become a self-fulfilling digital worker to work by itself without human intervention through self-learning based on pattern recognition and unstructured data. In some areas, including customer service, driving, and medical diagnosis, complete artificial intelligence beyond the level of RPA is developing to such an extent as to be able the role of a single person.
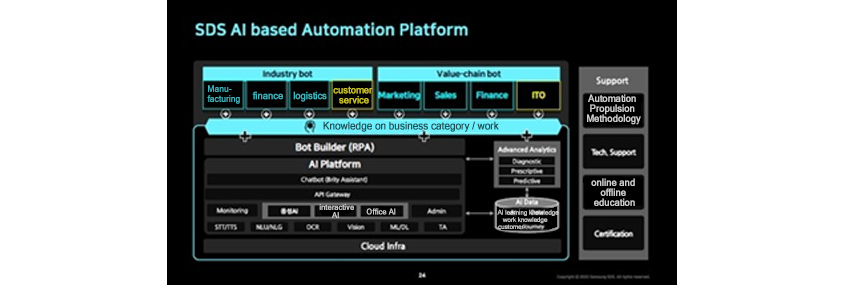
- industry bot/value-chain bot
- Manufacturing, finance, logistics, customer service/ marketing, sales, finance, ITO
- Knowledge on business category/work
- Bot builder (RPA), AI platform, chatbot (Brity), API (Marketing, interactive AI, Office AI admin)
- advanced anaysis
- AI data (AI learning knowledge, work knowledge, and customer)
- Knowledge on business category/work
- Bot builder (RPA), AI platform, chatbot (Brity), API (Marketing, interactive AI, Office AI admin)
- Cloud Infrastructure
- Support
- Automation method, online and offline education
RPA is a milestone, not a destination. So, we need to realize RPA than just consider it a starting line for utilizing and successfully incorporating our work. We need to focus on more creative and value-added work and find a new chance for business innovation in the time we are newly earning. And we need to develop RPA to cognitive automation for human-like inferences and judgments to get bigger help in handling more accurate and creative work. To do so, systems should be established to collect field data from a greater variety of industries and discover and automate new tasks for more RPA roles. For this process, Samsung SDS offers cognitive AI services, automation platforms, and cognitive platforms that work as a total platform with simple RPA development features and a responsive AI assistant solution, Brity Assistant, for easier RPA usage.
The future of the work changed by AI
There are many types of software for improving work besides RPA to save us from spending our time on unnecessary work. For example, you can download intelligent automated log generation apps on your smartphone that record voices and generate logs based on the recordings. The app takes notes on behalf of humans to help them remove the need to write bothersome logs. If an advanced form of AI assistants emerges in the future, they will automatically share the summary of important agendas with participants and send emails to the people in charge of the related department.
In addition, the “If This, Then That” (IFTTT) service offers automated services by connecting separate services and applications. In fact, this service can perform many automated functions in endless combinations, so I am a bit worried that my explanation could even limit your imagination. For example, the service can trigger sending an email to you, product planning, and marketing team leaders when information is posted, including tweets or pictures of the product or competitors' products on Twitter or Instagram. Likewise, software is evolving to improve productivity through facilitating the work automation software or services one needs.
Microsoft's SharePoint service is a collaboration tool for employees to write documents, communicate, and share their knowledge and information within the company. Microsoft gives us yet another development tool, PowerApps, which uses SharePoint to help develop apps for computers or smartphones. Individual can create their own software using those programs. Of course, they help you create a program even if you are not a developer. Python is the most rapidly spreading programming language in recent years and is used in various areas thanks to its concise structure and flexibility. Some courses have recently gained attention in that it trains non-developers and general users in developing simple programs.
PowerApps and Python are easy-to-use development tools that shatter the stereotype that only programmers can develop software. Thus, more people find the chance to create and use the software they need using those toolkits. Of course, the languages employed in those tools are still more difficult than just using smartphone apps. However, one day, each individual will be able to create and use optimized automation programs for everyday life and work when software development becomes easier. The era of citizen developers will come.
As such, RPA and automated software will help individuals maximize their capabilities in our workspace. Of course, AI will be a key player in developing RPA or personalized custom software.
▶ The content is protected by the copyright law and the copyright belongs to the author.
▶ The content is prohibited to copy or quote without the author's permission.

He’s interested in and studying how technologies make changes in our daily lives and society, and how they can be used for BM innovations in companies.
- Strategies for Building an Enterprise Document Streaming Service
- Brity RPA WORLD where Humans and Robots Collaborate
- Achieve Complete Task Automation with Brity Automation Platform!
- Brity RPA on a Mission to Rescue the Financial Industry from Repetitive Tasks!
- Leave Simple Manual Tasks to the Task Fairy, Brity RPA!
