Creating a consistently positive, seamless experience for customers can be particularly challenging for QSRs. However, restaurant brands that rely on real-time data insights rather than instinct can make more informed decisions, as well as implement uniform improvements across locations. As such, those QSRs will be better positioned to create the positive experience the customer expects.
Taking a holistic approach
Holistic approaches to collecting and interpreting in-store analytics effectively combine data, communication, technology and organizational execution to ensure QSRs can implement profitable programs that introduce positive change at scale. Take, for example, the Customer Operating Zone Improvement research and development approach. COZI recognizes that every restaurant has individual operating zones, within which customers behave differently. For instance, QSRs typically have zones for entering, lining up, ordering, paying, getting beverages, picking up orders, dining and exiting. If restaurant managers identify these zones and understand how consumers interact in each one, they can produce zone-specific posters, signs, menu boards, window decals and other displays with targeted messaging that complement customer needs within each area of the restaurant. Such consumer data can also influence an optimal restaurant layout, including where to route the line or how to configure dining tables.
Case in point: When Starbucks conducted a COZI analysis, the results revealed that the drive-thrus lacked the barista-driven ordering experience consumers had come to love - and positively associate with the brand. The coffeehouse chain responded by introducing video baristas to their drive-thrus, an upgrade that became the largest capital program in the company’s history to that point. Through zone analysis, Starbucks also discovered that there were specific saturation points for marketing and messaging within individual zones. Once a customer saturation point is reached, additional investment leads to wasted resources and detract from the customer experience. As a result of these findings, Starbucks developed guidelines that enabled them to better manage messaging, increase purchases, and optimize the customer experience.
Collecting and applying the data
Of course, consumer behavior data is at the heart of such analysis and strategic improvement. Quick serve managers can gather the information from operations data, product sales reports, labor statistics, surveys and consumer focus groups. Behavior sensing technology, such as heatmap analysis and zone counting, can also reveal data-driven answers to key questions at highly efficient speeds.
QSR solutions like Samsung Nexshop Behavior Sensing make it easy for restaurant operators to collect real-time customer data analytics. The technology provides managers with powerful insights into their consumer base, such as:
• Demographic breakdown of customers, including gender and age
• The number of people in line
• Average wait time
• Peak ordering times
• Popularity of ordering methods, such as counter, mobile kiosk or drive-thru
• Foot traffic patterns
• Zone count and behaviors
These analytics can help managers optimize the back of the house, such as strategic scheduling and employee placement for peak ordering times. Objective camera sensors can measure real-time traffic flow to report on statistical trends. Zone counting and heat mapping data further unveil insights into where people are in the restaurant and how they interact in those areas, which can influence optimal store layout and display placement.
For example, a recent study revealed that 86% of consumers admit leaving retail stores because of long lines, resulting in loss of interest and sales. What’s more, retailers lose over $1 billion in sales when they don’t support preferred payment methods. For QSRs, this can mean losses in brand equity and sales, as well as financial hurdles from labor inefficiencies and food waste. However, real-time behavioral analytics can help QSRs understand these challenges and correct the issues before consumers choose to eat elsewhere.
As a significant driver of QSR sales, drive-thru experiences can especially benefit from behavioral analytics. Not only can the data inform strategic upgrades, but the technology can also help restaurant operators monitor performance and highlight where there’s room for additional improvement. Everything from kitchen layout to menu boards can influence the speed, convenience and accuracy of drive-thru orders, making the data-driven insights a helpful tool for creating an ideal customer drive-thru journey.
The technology also proves useful for increasing QSR marketing effectiveness. For instance, tracking information about customer proximity to the restaurant as well as time spent inside can guide strategic signage placement. Analysis of customer behavior and sales can also help marketers determine how effective the messages were in encouraging customers to enter the QSR or buy certain products. Furthermore, customer demographic information helps marketers create more targeted content and promotions.
While digital displays and other technology can improve the QSR experience, behavioral analytics is about using data to better understand the consumer. That way, QSRs can implement the digital solutions that will resonate with customers, rather than using the technology for the sake of it. This strategic decision-making yields better results for digital transformation projects. The Starbucks video baristas, for instance, serve a true customer-service purpose by making the convenient drive-thru experience more reminiscent of ordering inside. Smart ordering and intelligent greeting signage further increase customer convenience and satisfaction.
From a corporate standpoint, working with a QSR solutions vendor can further help restaurant operators centralize their digital transformation efforts, as well as ensure the data they’re collecting doesn’t contain any personal identifiable information.
Unleashing the untapped potential of AI and machine learning
It’s clear that digital transformation is disrupting the QSR industry in deep and fundamental ways. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are major players in the digital revolution for QSRs as well as companies spanning various industries. According to Gartner, augmented analytics focused on machine learning are transforming how all content is developed, consumed and shared, and, as a result, will likely see mainstream adoption by 2020. AI-powered devices are no longer new to QSR customers, but how quick serves decide to implement the technology has the potential to impress them.
QSRs can use AI and machine learning to improve the guest experience and increase revenue while simultaneously reducing operational complexity. Along with powering the data collection and behavioral analytics tools that drive digital-first strategies, the advanced technology automates menial tasks for significant increases in QSR speed and accuracy.
Manage QSR employees and supplies
AI is an especially effective tool for solving QSR labor issues before they have a negative impact on customer experiences. Notorious for high turnover rates, QSRs can use advanced technology to enhance operational efficiency, support customer service initiatives and increase revenue despite the ever-changing workforce. Digital customer service solutions, for example, leverage machine learning to automate the repetitive and tedious elements of food orders. With touchscreen technology and voice-ordering, these digital representatives can record consumer selections, make personalized recommendations and improve order speed and accuracy. The technology seamlessly and continuously learns from each interaction to provide even more nuanced, natural and helpful exchanges with consumers.
These digital solutions can also help QSRs overcome labor and supply shortages during peak hours and eliminate human-related challenges, such as time-off requests and fatigue. AI technology further powers improved scheduling capabilities to relieve managers from time-consuming and complex tasks. Scheduling software can predict labor demand, allow employees to swap shifts with little managerial involvement and factor in details like employee performance and history to schedule optimal teams for sales and customer service. From an inventory perspective, AI automatically tracks food sales to ensure appropriate supply levels and reduce waste at each location.
Enhance consumer experiences
AI-powered recognition technology further plays a significant role in the future of personalized drive-thru experiences by making recommendations based on customer profiles. Voice-ordering technology can also present custom upsell messages that make recommendations based on the weather, current promotions or consumer inquiries.
The advanced technology also increases the chances that QSRs meet the standards of order accuracy and speed expected from a drive-thru experience. According to the 2018 QSR Drive-Thru Study, drive-thru orders are inaccurate more than 10% of the time and high employee turnover rates significantly slow average speed-of-service time. AI and machine learning can take over recording and processing orders, reducing the likelihood of human error and enabling employees to focus more of their attention on the in-person interaction at the service window. With improved order accuracy, decreased wait times and enhanced interactions, both customers and employees experience a surge in satisfaction. Additionally, BCG estimated that labor savings in the drive-thru segment of QSRs could reach upward of $100 million for large brands.
By managing drive-thru orders, AI can also help franchisee managers comply with service agreements that require multiple lanes to be open during certain hours of the day without facing staffing or operational hurdles. Plus, the more lanes that are open, the less time customers have to wait to place and receive their orders.
Inside quick serves, AI enables the self-order experience. Studies show that self-serve kiosks and digital displays give guests more time to study product photos, ingredients and nutritional information, which ultimately encourages them to purchase more. Self-serve also eliminates transactional demands at the counter, resulting in shorter lines and additional time for employees to focus on other customer-service tasks.
In a similar vein, restaurants can modernize elements of the customer experience with augmented and virtual reality technology. For instance, guests may don VR headsets to learn more about the products or company when deciding what to order or while waiting for their food. QSRs can also augment employee training with VR and gamification. The fast-casual chain Honeygrow created a food-safety game with VR headsets that requires employees to select the correct locations for vegetables and raw meats. The virtual onboarding tool improved training consistency across locations, relieved managers from the responsibility of leading the sessions and reduced employee training costs.
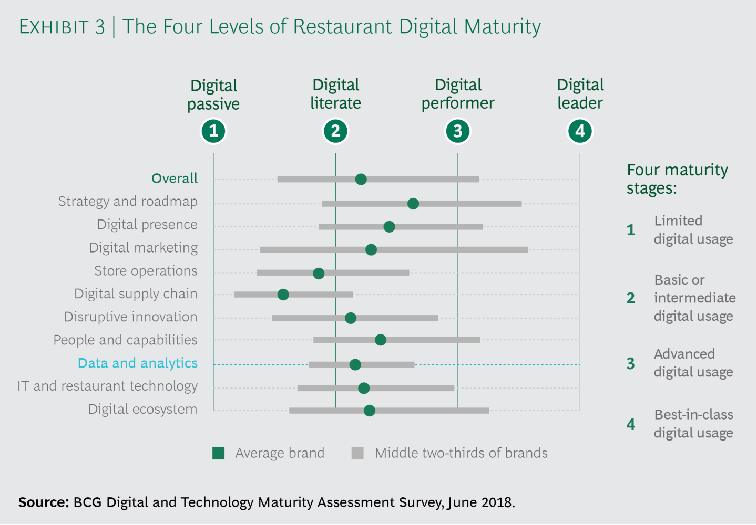
With increasing accessibility and affordability, these advanced technological solutions are becoming more feasible options for QSR digital transformation. However, the potential is still there for QSRs to spearhead new applications of AI and machine learning. In a digital maturity survey conducted by BCG, only 1 in 5 of top restaurant brands reported having big data strategies in place. Few to none considered their company to be fluent in advanced analytics techniques such as AI and machine learning. As such, there is a sense of urgency for quick serves to reach their tech-savvy consumer bases before it becomes commonplace among competitors.

Maggie is part of the Digital Transformation Team at Samsung SDS America.
- 3 steps to optimizing the car dealership showroom experience
- How to enhance modern dealership operations: Inventory, staffing, and showroom management
- Reducing costs with affordable and resourceful mPOS
- Improving the user experience with mPOS
- Mobile point-of-sale systems: How they streamline the user experience & maximize ROI
- Making inroads into QSR digital transformation
